Lupine Publishers | LOJ Medical Sciences
Introduction
Today insect pests have
been one of most important problem in food production. Previous research have
been proved that 1/3 of agricultural production of world, prized at several
billion dollars is ruined by damaging of field and storage insect pests every year.
Various toxic, broad-spectrum and synthetic chemicals are used to control
pests. Natural ecosystem, human health and our environment can be affected due
to excessive use of these harmful chemicals. So now biologically based
approaches are developing to control insect pest instead of toxic and synthetic
chemicals which are ecofriendly, cost-effective and useful and reliable. There
are different types of bio pesticides such as arthropods natural enemies
(predators, parasitoids, and parasites), entomopathogens (bacteria, fungi,
virus and nematodes), insect hormones and plant derived bio pesticides.
Role of Biotechnology
It is a set of techniques for manipulation of living organisms or
their components to produce useful commercial products such as new bacterial
strains, pest resistant crops. There are various techniques are used in
biotechnology like biological fixation of nitrogen, tissue culture and organic
pest control. Previous research have been proved that Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) was discovered in 1906
by mortality of silkworm larvae. Bacillus thuringiensis stands
out on the world stage since 1938, when first product was formulated with this
pathogen released in France. In 1911 A German scientist Berliner succeeded to
detach and characterize this bacterium has cylindrical shape and
“thuringiensis” named after German region “Thuringia”. In1938 France
formulations having bacteria colonies was sold as an insecticides. In 1954 Mode
of action was revealed and its usage today. Bt is known as soil bacteria which
is found in different countries, Gram positive, aerobic and its family is bacilaceae.
It can sporulate to
survive when environmental conditions become adverse and unfavorable. This is
found in dead insects, plants and debris. This produces sporangia containing
endospores and crystalline inclusions of proteins (CRY) which are responsible
for their action against lepidopterans insects. This Crystal is composed of
polypeptide protein that is called endotoxin. When larvae feed on such proteins
initiates the number of reactions that kills them.
Biotechnology Better Than Insecticides:
Recent researches have
been found that insect pests are major problem for agricultural crops, and
losses due to diseases and insect pests are very high.to manage insect pests we
use various harmful agrochemicals day by day on large scale and use bio
pesticides just on small scale. Survival of natural enemies (predators,
parasitoids and parasites), human health, beneficial insects, and environment
are badly affected by unselective use of chemicals. It also produce resistance
in insects against agro chemicals. On the other hand, Bio pesticides used over
a country which is less harmful for environment and human beings than synthetic
chemicals. To control insect pests’ new strategy has been developed which
consists of genetically modified plants resistance against insects, and they
are similar and effective like conventional insecticides. In 1986 the first
experiments with genetically modified (GM) plants were made in the United States
and in France.
The first variety
marketed a vegetable species produced by genetic engineering was the “FlavrSavr
Tomato” developed by the American company Celgene and marketed from 1994. 1987-
2000 there were more than 11,000 field trials in 45 countries and tested were
corn, tomatoes, soybeans, canola, potatoes and cotton, and development of safer
and more effective technologies genetic features announced were herbicide
tolerance, product quality, virus-resistance and resistance to insects (Table
1).
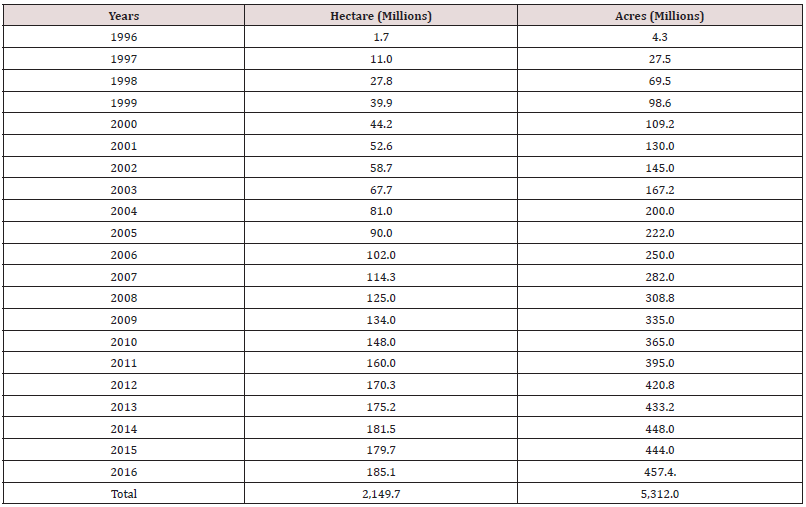
Table 1: Worldwide Area of Biotech Crops from 1996-2016.
Area of Biotech Crops in developing and industrial countries:
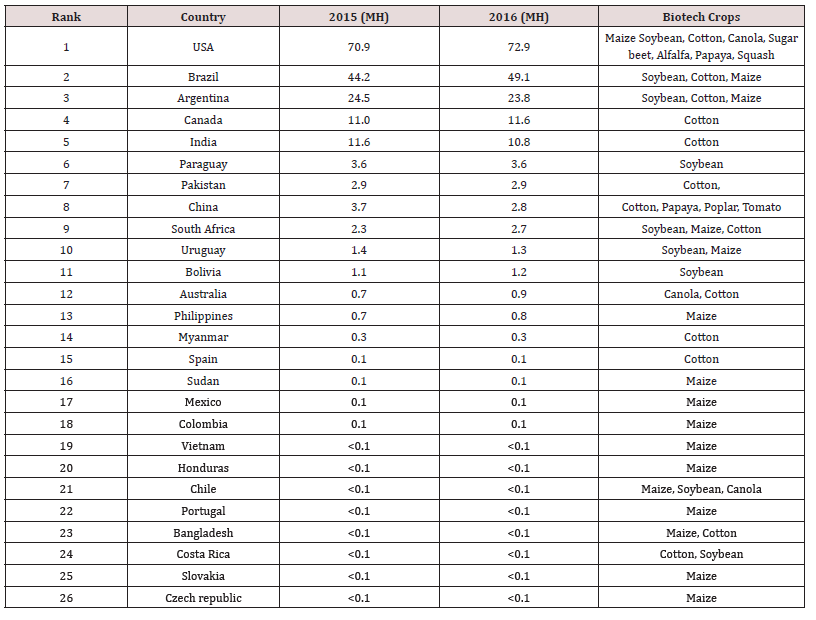
In 2016, 19 developing countries cultivated 54% biotech crops on 99.6 million hectares out of worldwide biotech cultivation area while 46% biotech crops were planted on 85.5 million hectares in industrial countries.A new biotech crop rice which is grown in developing countries (Table 2).
Mode of Action of Cry in Bt Cotton:
This protein is inactive
protein. This requires Alkaline Ph. (7.5- 8) for activation. This is only
harmful for lepidopterist insects and not for sucking insects and other
organisms because lepdopterous insects have this alkaline ph. medium which is
required for activation of Cry. When insect attacks on cotton plant this toxin
enters into body and become activate. Active toxin binds with protein receptors
on epithelial cells within midgut. Then this toxin forms pores and puncture the
midget so insect will be die due to starvation.
Major applications of Cry toxins
i. Control of deflator
pests
ii. Control of
mosquitoes which cause a vector for human diseases
iii. Development of
transgenic crops

No comments:
Post a Comment