Wednesday, 19 February 2020
Lupine Publishers: Lupine publishers | Modern Tools and Techniques fo...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine publishers | Modern Tools and Techniques fo...: Lupine Publishers | Agriculture Open Access Journal Introduction Soil salinity and brackish ground water are primary concerns for r...
Friday, 14 February 2020
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | The Dynamics of Mounds-Cluster...
Lupine Publishers: Lupine Publishers | The Dynamics of Mounds-Cluster...: Lupine Publishers- Anthropological and Archaeological Sciences Journal Impact Factor Abstract Mounds are human made accumulations ...
Wednesday, 12 February 2020
Lupine Publishers | The Effects of The Leaf Extracts of Vernonia Amygdalina, Ocimum Gratissimum and Phyllanthus Amarus on Blood Glucose Level of Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Guinea Pigs
Lupine Publishers | Lupine Online Journal of Medical Sciences
Abstract
Introduction
These selected tropical herbs used in this study are extensively applied by herbalists and taxonomists or several medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus. The major emphasis is on their aqueous leaf extracts. Vernonia Amygdalina (bitter leaf) is a tropical shrub in the plant family of composite. The leaves are widely used as vegetables probably because of its therapeutic properties. Those who consumes, bitter leaf regularly stands a better chance of being prevented from developing diabetic and hypertensive complications [5]. The leaves of vernonia amygdalina are given with a characteristic odor and bitter taste attributed to anti-nutritional factors including alkaloids, saponins, tannins, glycosides, sesquiterpenes flavonoids as seen in phytochemical screening [6]. Strong anti-oxidant activities have been reported for flavonoids from vernonia amygdalina and its saponins have been reported to elicit anti-tumoral activities in leukemic cells [7].
Ocimum gratissimum
Ocimum gratissimum commonly called Scent leaf is an herbaceous perennial herb and wood at its base. It is commonly used in preparing foods owing to its spicy nature apart from its therapeutic importance. This herb is in the family of Labitae, and it is widely seen in Africa, east India and Brazil. It comprises of green leaves, stem and roots.The aqueous extract of ocimum gratissium has a hypoglycemic effect which is due to methanolic extract of the leaves which enhance its hypoglycemic activity. The extracts contain essential oil. The essential oil is anti-protozoan. It inhibits the growth of protozoan [8]. Antibiotic effects have been associated with the extract of ocimum gratissimum leaves. This is basically due to its essential oil. The essential oil in ocimum gratissimum has been found to inhibit staphylococcus. Aside the essential oil, the methanol extract has antibiotic properties and facilitates wound healing [9]. Phyllanthus amarus commonly called stone-breaker is a perennial herb grown in the tropical forest such as Africa. It is also seen in china and Asia. This herb has tiny green leaves and soft stems. It is in the family of Euphorbiaceous. The extract of phyllanthus amarus has been widely found and used in diabetic management by some herbalists probably due to its hypoglycemic effects. Aside its application in diabetic management, it has also been found useful in viral hepatitis including chronic hepatitis. Its extracts are said to be hepato-protective and it’s used in the herbal treatment o primary hepatocellular carcinoma [10].Materials and Methods
Experimental animals/grouping
Thirty-five guinea pigs of different sexes were randomly selected for this study and weighed with a weighing scale before administration of any substance or induction with alloxan. The average weight of the guinea pigs was 250grams body weight. These guinea pigs were grouped into five groups with five guinea pigs in each group. The first three groups were for the substances or extract used for the study. While the remaining two groups were for the negative and positive control groups with oral administration of 0.9% N/S (Physiological solution) and solution of Glibenclamide (Oral hypoglycemic) respectively. All the grouped guinea pigs were intraperitoneally induced with a single dose of 5% alloxan monohydrate dissolved in 0.9% Normal saline after determining their fasting blood sugar with a glucometer (Pre-induction fasting blood sugar).Ocimum gratissimum
Those for the preliminary test were induced with a single dose of alloxan intraperitoneally at concentration of 100ml/dl, 150ml/ dl and 200mg/dl for the respective groups as to determine the optimal concentration of alloxan that will bring about a significant increase in fasting blood sugar three days post alloxan induction in three consecutive readings. The three main groups of guinea pigs were induced with a single dose of alloxan intraperitoneally with 200mg/kg body weight with a 2ml syringe to make them diabetic after blood sugar level pre-alloxan induction had been taken by the glucometer. These guinea pigs were fed with elephant grasses and fasted for 9 hours in each reading.Aqueous leaf extract of the fresh leaves of these tropical herbs were obtained by squeezing one kg each bunch of fresh leaves in 280 mls of water in different washing basin and thereafter received in different labeled bottles after sieving. Prior to extraction, the leaves were bought from the local market aside the phyllanthus amarus which was gotten from the bush. These leaves were identified by staff of department of Plant Science University of Port Harcourt. The aqueous leaf extracts were given per oral with a canula at 300mg/ kg body weight to the grouped alloxan induced diabetic guinea pigs. Solution of glibenclamide at 0.25mg/day orally was given via canula to the positive control group post alloxan induction. In the same manner, 0.9% normal saline was also administered orally via canula to the diabetic induced negative control group. The fasting blood sugar level was determined after three consecutive days for two weeks and then the mean values determined. The aqueous leaf extracts were taken for phytochemical analysis at the department of Biochemistry, Macdonald University Elele, and Rivers State.
Phytochemical screening
The phytochemical screening (test) was done in the department of Biochemistry Macdonald University Elele, Rivers State. Phytochemical screening of the six aqueous leaf extracts under study was carried out on the crude methanolic extract and the weakly acidic fraction using standard procedure and reagent outlined by Harbourine [11]. In general, test for the presence or absence of phytochemical compounds using the above method involving the addition of an appropriate chemical reagent to the tests sample in a test tube. The presence or absence of the phytochemical compounds in each extract was established. These phytochemical compounds are saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins, carbohydrates such as glucosides (reducing sugars), proteins, resins, oil, steroids and terpenes. All the extracts were tested for these above phytochemical compounds.Discussion
Table 1: The preliminary tests showing differential increase in mean fasting blood sugar level after alloxan induction at concentration
of 100mg/kg and 200ml/kg.
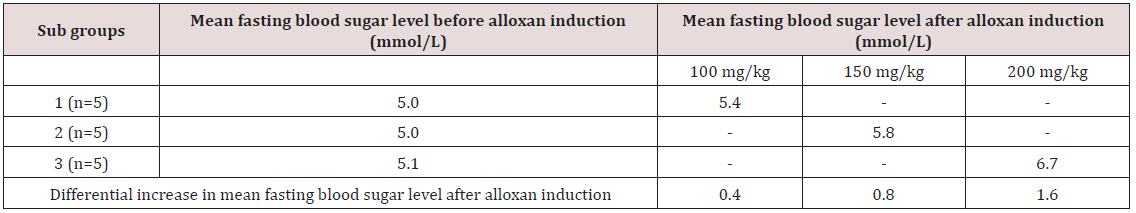

Table 2: The percentage reduction of mean fasting blood sugar level readings obtained from induced groups of guinea pigs with
alloxan (200mg/kg) after administration of aqueous leaf extracts using 0.9% normal saline and Globenclamide solution as negative
and positive control groups respectively.
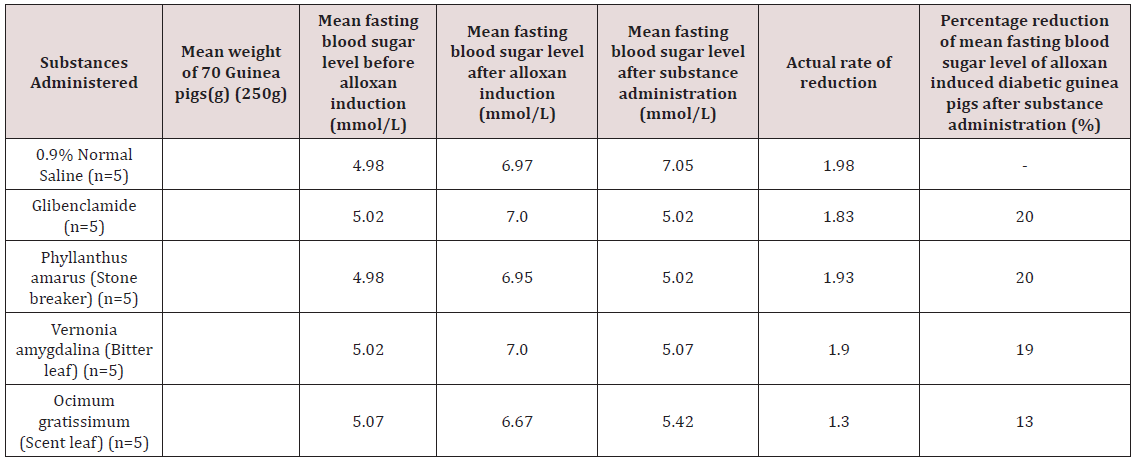
Ocimum gratissimum aqueous leaf extracts also showed
moderate percentage reduction of 13% respectively which were
less than the readings from positive control group of 20% reduction
in mean fasting blood sugar level after those extracts. The negative
control group of diabetic guinea pigs that had 0.9% Normal saline
which is a physiological solution revealed no percentage reduction
of blood sugar level. Using ANOVA as the statistical analytic methods,
mean fasting blood sugar level of different groups as shown in this
Table 3 before alloxan induction could be compared with fasting
blood sugar level after alloxan induction. This Table 3 indicates that
there was a significant difference between the mean fasting blood
level before and after alloxan induction in all the groups (p<0.05).
Also, in Table 4, Using Z-Test to compare the mean fasting blood
sugar level of these guinea pigs after alloxan induction and mean
fasting blood sugar after substance administration, a significant
difference was seen in groups of guinea pigs that had glibenclamide
solution and those that had aqueous leaf extracts of phyllanthus
amarus, vernonia amygdalina and ocimum gratissimum (P<0.05).
This indicates that the mean fasting blood sugar level of the
groups of guinea pigs that had these aqueous leaf extracts above
is comparable to the mean fasting blood sugar level of the positive
control group that had glibenclamide (oral hypoglycemic agent).
Table 3: The mean fasting blood sugar level of the grouped guinea pigs before and after alloxan induction using ANOVA as the
statistical analytic method as seen in the table above.
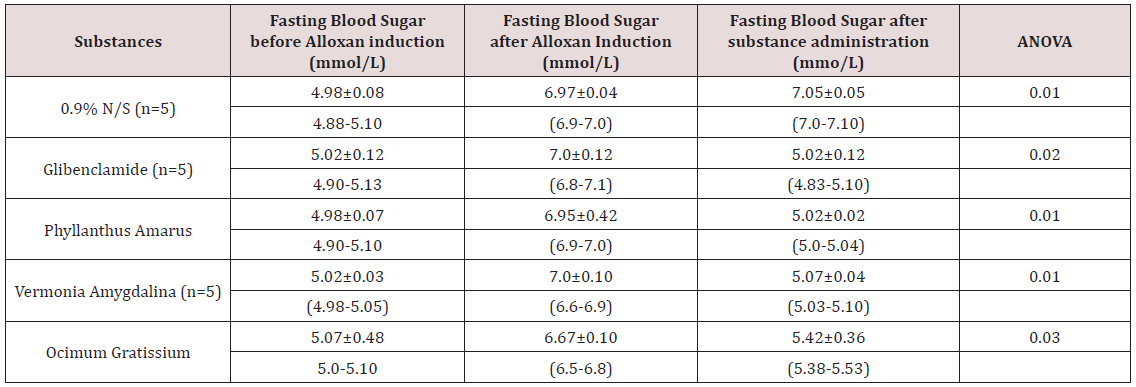

Table 4: Comparison between the mean fasting blood sugar level of the grouped guinea pigs after alloxan induction and after
substance administration using Z-Test.
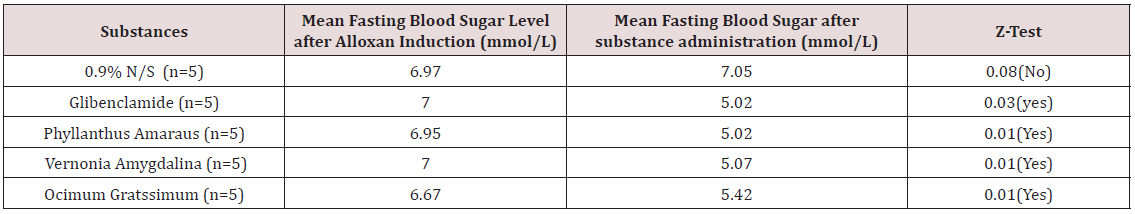
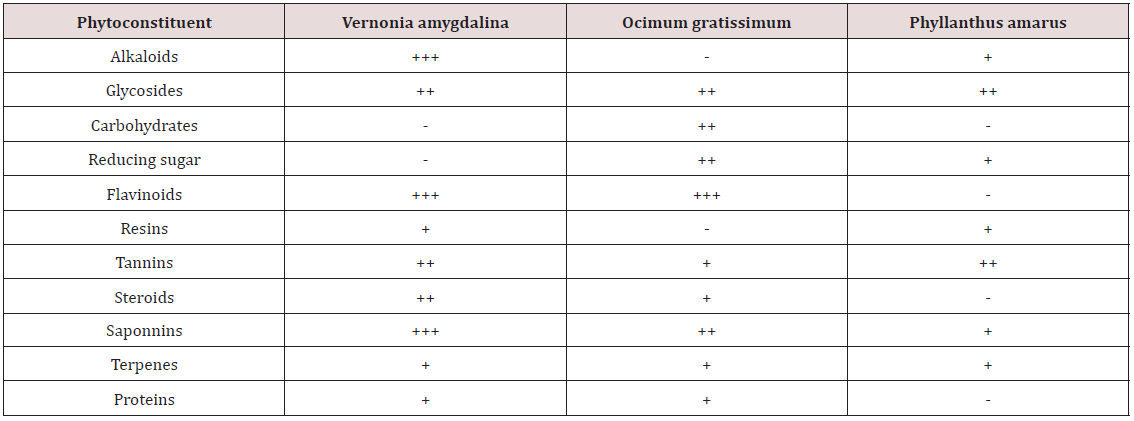
Table 5 represented above showed the quantity of the
phytochemical constituents in each aqueous leaf extract of these
tropical herbs during the phytochemical analysis. The presence of
these phytochemical constituents is related to the hypoglycemic
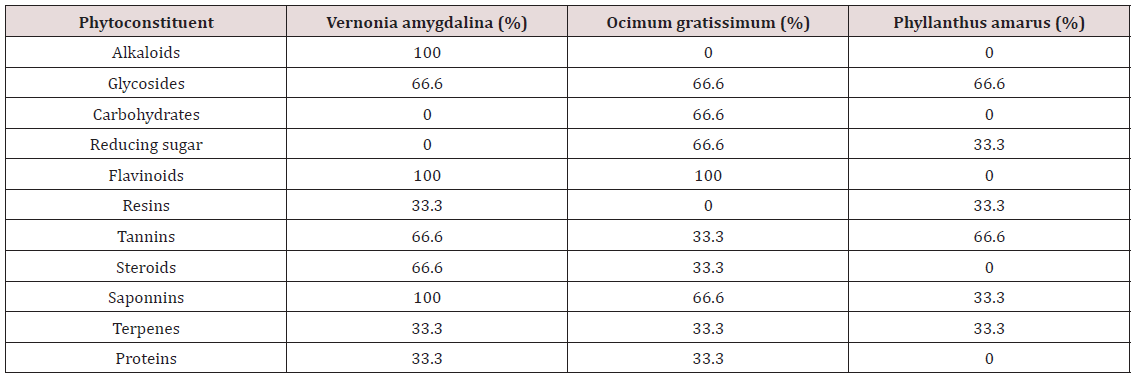
potency. In Table 6, the quantity of phytochemical constituents
of these aqueous leaf extracts was expressed in percentages. The
result obtained from the phytochemical screening of these aqueous
leaf extracts as shown in Table 5 & 6 indicated that Vernonia
amygdalina contains moderate levels of Alkaloids, Saponnine,
Flavinoids at 100% composition and glycosides, tannins, Steroids
at 66.6% composition with mild levels of Resins, terpenes and
Proteins at 33.3% composition. In other words, there are more
alkaloids, flavonoids, saponnins than other phytochemical
compounds in vernonia amygdalina. This extract contains no
carbohydrates or reducing sugars. The presence of many of these
phytochemical constituents in appreciable quantities up to 100%
and the absence of carbohydrate including reducing sugars may be
responsible for its high hypoglycemic potency [12-25].
Table 5: The quantitative analysis obtained from phytochemical screening of the aqueous leaf extracts.
= absence of the phytochemical compound
= = presence of the phytochemical compound.

= = presence of the phytochemical compound.
Table 6: The percentage composition of the phytochemical constituents found in phytochemical screening of the aqueous leaf extracts
of these three tropical herbs used for the study.
% = percentage composition of Phytochemical constituents in extracts.
Phyllanthus amarus was found to have moderate levels of
glycosides and tannins at 66.6% each, with mild level of reducing
sugars, resins, saponins and terpenes at 33.3% composition. It was
also found to contain no alkaloids, carbohydrates aside reducing
sugars, flavonoids, steroids and proteins. The aqueous leaf extracts
of this herb contain more of glycosides and tannins than any
other phytochemical compounds. The saponins in this extract is
far less than that of vernonia amygdalina but contains the same
quantity of tannins and resins. The absence for its hypoglycemic
effect. It has been noted that steroids are diabatagenic. Ocimum
gratissimum contained moderate levels of flavonoids, glycosides
and carbohydrates, reducing sugars and saponins at 66.6% each
during phytochemical screening. The glycosides and terpenes were
found to be of the same quantity as in the above two extracts. The
saponins in this leaf extracts are less than the quantity obtained
from vernonia amygdalina but contained the same quantity
of flavonoids at 100% composition. However, flavonoids as a
phytochemical constituent has antioxidation effect while saponins
and peptides have antitumoral effects as stated in the early part of
this work.
Conclusion
Follow on Linkedin : https://www.linkedin.com/company/lupinepublishers
Follow on Twitter : https://twitter.com/lupine_online
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
The Body Electric: Humans Have A ‘Force Field’ Around Their Bodies
Abstract Bioelectronic medicine (BEM) is the most recent medical revolution — not an innovation or an improvement or a step up but a radic...
